Glucometer is a glucose-lowering medication that inhibits AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and mitochondrial complex I. However, this medicine is not without side effects and should only be used under the supervision of a doctor. Children and elderly people should also use the drug with caution as they are more susceptible to low blood sugar levels.
Table of Contents
Glucometer is an anti-diabetic

Glycomet Tablet is a prescription medicine that lowers the blood glucose level of people suffering from type 2 diabetes. It works by reducing glucose production in the liver and slowing down the absorption of sugar from the intestines. It also improves the body's sensitivity to insulin. This medication is an important part of managing diabetes, as it can prevent the development of complications that are associated with high blood glucose levels. If taken regularly, Glycomet Tablet can help the patient lead a normal life.
Glucomet is prescribed to patients with Type 2 diabetes who have a high blood sugar level and have failed to control their blood sugar levels through exercise and dietary changes. Patients are advised to take a single 500 mg tablet daily at a fixed time.
Glycomet Tablet 10 can interact with a number of medications, including some heart conditions and anti-depressants. If you're taking any of these medications, talk with your doctor before beginning Glycomet. Your doctor may adjust the dosage if needed. In addition, patients should eat frequently and avoid long meals. They should also check their blood sugar levels regularly. People with diabetes should also try to get at least 150 minutes of moderate or high intensity physical activity every week. It's also important to lose weight slowly in order to achieve a healthy body mass index.
Glycomet-GP 1 Tablet PR is a combination of two medicines called Glimepiride and Metformin. It helps the pancreas produce more insulin and lowers blood glucose levels in adults. It also reduces glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity. However, it is not recommended for people with type 1 diabetes.
It inhibits mitochondrial complex I
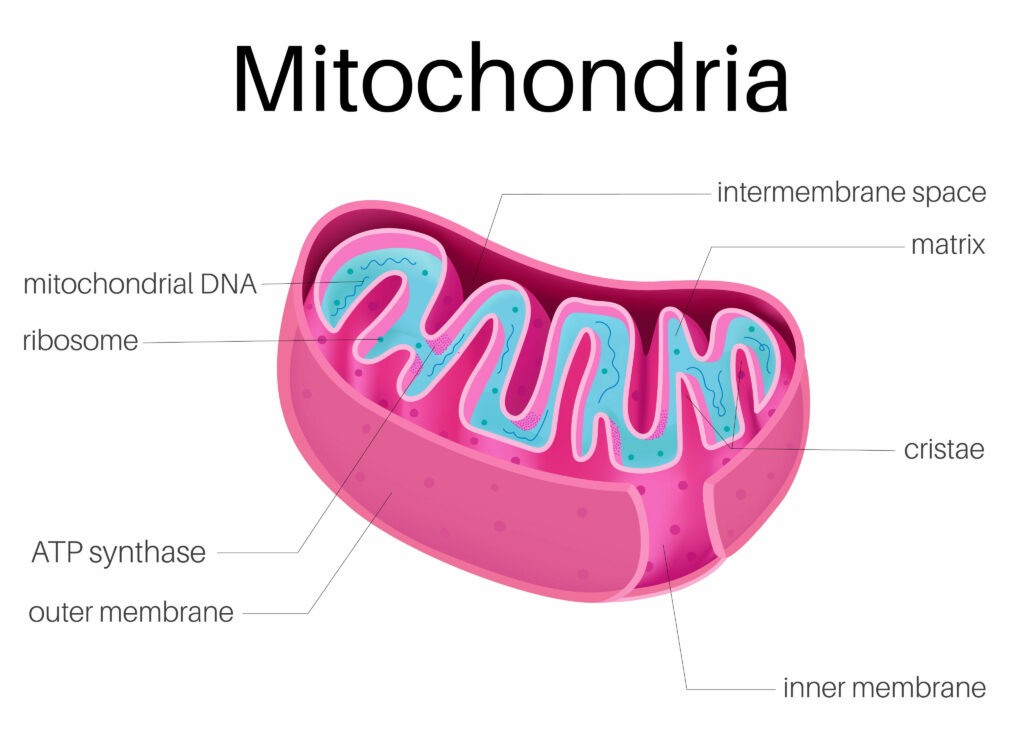
The aim of the study was to provide a comprehensive understanding of how mitochondrial complex I malfunctions in diabetes mellitus. This was done by using mouse models of early and late stages of type I diabetes, pre-diabetic mice, and mice that had been induced with high-fat diet (HFD). The mice were selected for their ability to demonstrate the full range of disease symptoms.
In addition to inhibiting complex I, glucomet inhibits complex III in the mitochondrial membrane, which is the first step in oxidative phosphorylation. It also inhibits the production of mitochondrial ATP and decreases the ADP-to-ATP ratio. It has also been shown that metformin inhibits the activity of AMPK, which is essential for the metabolism of glucose.
In the study, 180 rats were divided into two equal groups and were injected intraperitoneally with streptozotocin 45 mg/kg. After one month, one-third of each group was sacrificed. In both groups, mitochondria were isolated from the liver and kidney. After this, oxygen consumption of complex IV (the enzyme responsible for energy production) was determined. After the assay, proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and compared with the values of control rats.
Metformin and glucomet are used to treat patients with type 2 diabetes. They lower blood glucose levels by inhibiting glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, and increase insulin sensitivity. These actions result in improved peripheral glucose uptake and delayed intestinal glucose absorption.
The effects of glucomet inhibition on cardiac function were studied in obese mice with diabetes mellitus and healthy controls. The drug reduced oxidative stress and lowered ROS levels in diabetic mice. In addition, it increased expression of genes related to FAO.
It inhibits AMP-activated protein kinase
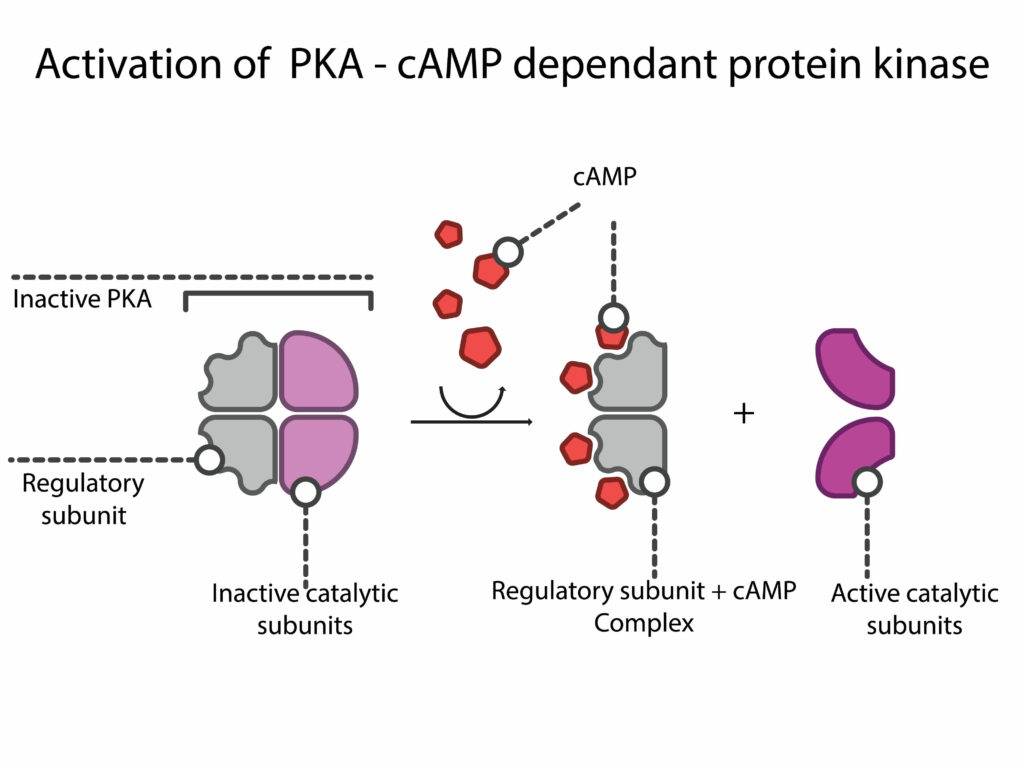
The AMP-activated protein kinases (AMPK) are important targets in metabolic diseases, including diabetes. They regulate fatty acid oxidation, glucose uptake, and mitochondrial biogenesis. Researchers have been reporting the presence of AMPK activators in natural products for decades. One example is the polyphenol resveratrol, which is isolated from grapes and has shown promise in the treatment of diabetic-related disorders.
The kinase is essential for glucose transport in skeletal muscle, including hyperosmolarity-induced glucose transport. In addition, AMPK has required for exercise mimetic effects. Therefore, Glucomet inhibits AMPK activity.
Metformin has a broad spectrum of action, although its cellular mechanism of action is not clearly understood. It is known to reduce hepatic glucose production and increase glucose utilization. It also reduces the levels of circulating lipids and has a beneficial effect on fatty liver. AMPK is a key regulator of lipid metabolism and has been implicated in metformin's action.
It can reduce the effectiveness of other medicines
One thing to remember when using Glucomet is that it can interact with other medicines. If you are currently taking any other medicines, you should inform your doctor about all of them, so that he can determine the best course of treatment for you. Some examples of such interactions include heartburn medicines, diuretics, corticosteroids, phenytoin, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin II receptors.