If you're curious about the OGTT, or the two-hour glucose tolerance test, read on. In this article, we'll cover how this test is used, and which types of diabetes are affected by it. We'll cover everything you need to know about the test, from type 1 to type 2.
Table of Contents
Diabetes
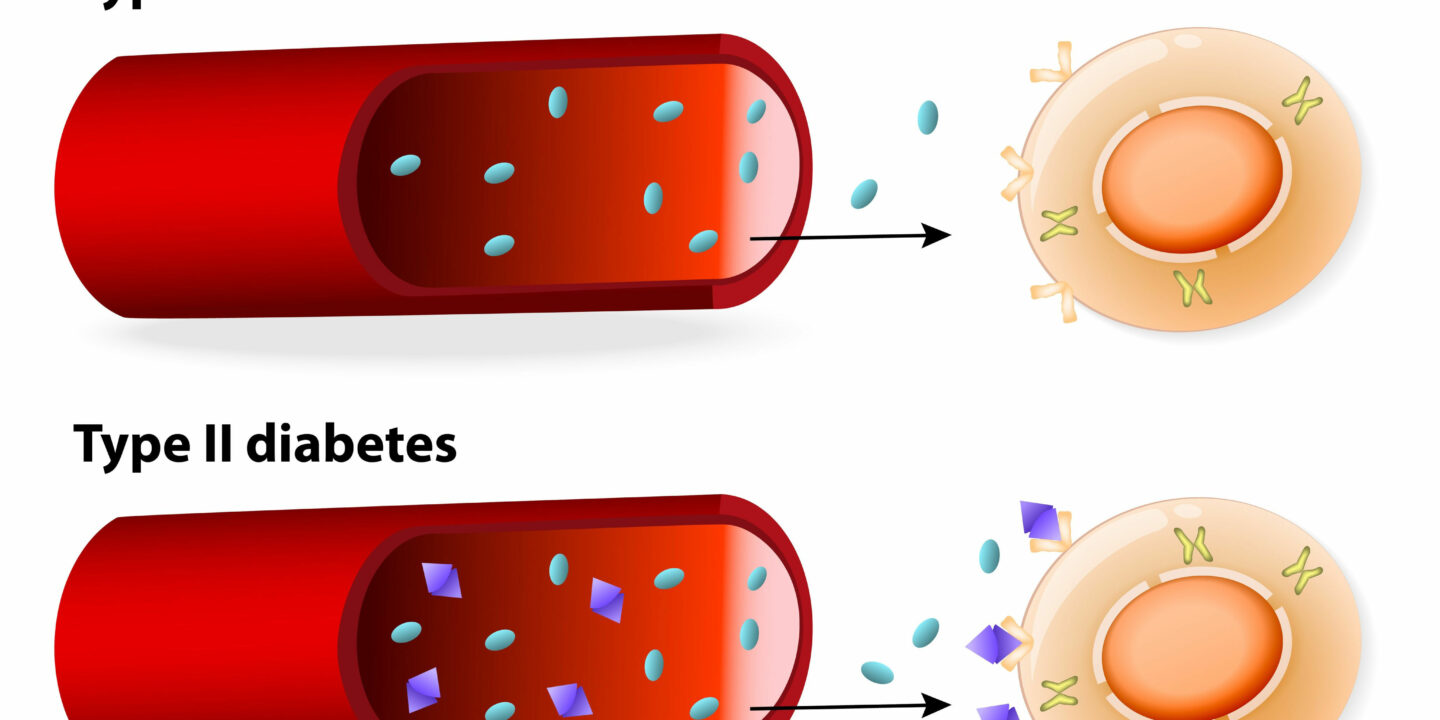
The glucose tolerance test is a blood test that measures your blood glucose level. Usually, the test measures blood glucose levels in milligrams per deciliter. This test can be conducted in your doctor's office, clinic, or laboratory. This test requires blood samples to be drawn and analyzed by a laboratory technician. However, it is not the only way to diagnose diabetes. There are other tests your doctor can perform to determine whether you have the condition.
To take a 2 hour glucose tolerance test for diabetes, you must fast for at least eight hours prior to the test. You should also schedule the test early in the morning. If you don't fast for at least eight hours, you can schedule the test for the next morning. It is important to fast completely before undergoing the test so that your body is ready for the glucose challenge. The test is not accurate if you are already consuming glucose.
The blood glucose values of a person with diabetes reflect the balance between glucose absorbed from the gut and the insulin produced by the pancreas. These values reflect the fasting blood glucose level, the glucose load, and the two-hour test. These blood glucose levels are often used to diagnose diabetes. During a fasting period, you should consume at least 8 ounces of water. During the test, you must be at least 140 grams of food or drink. The glucose levels in your blood should fall back to normal within two hours.
OGTT

The OGTT, or two-hour glucose tolerance test, is a clinical laboratory test to measure blood glucose levels. In a healthy individual, blood glucose levels will stay within a normal range. When this is not the case, high blood sugar levels may lead to diabetes or hyperglycemia. Several different conditions can lead to high blood glucose, including insulin resistance and lack of insulin. Reactive hypoglycemia, acromegaly, and other disorders of glucose metabolism may also be caused by high blood glucose levels.
To prepare for the OGTT, you should fast for at least eight hours before the test. You should also refrain from drinking alcohol, smoking, or engaging in any physical activity for at least eight hours before the test. Additionally, you should let your healthcare professional know about any medication you're currently taking, as they may advise against it before the test. The OGTT is performed in a medical office, clinic, or hospital.
The OGTT is a more sensitive and specific test than a fasting blood glucose test. It is often ordered if you suspect you have diabetes but haven't yet consumed a meal. Unlike a fasting plasma glucose test, the OGTT allows your doctor to detect any impairment early, when treatment is easier. Additionally, it is the only test that can definitively diagnose IGT. However, it is difficult to perform and can be expensive. The patient must fast for at least eight hours before the test and wait a long time for the results to be available. Moreover, a patient's stress level and blood storage conditions can influence the result.
OGTT for type 1 diabetes
The two-hour glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is a screening test for diabetes. It is used to confirm the presence of diabetes when other tests fail to diagnose it. To perform the test, people are given 50 grams of glucose orally and a blood sample is taken one hour later. If the glucose level is normal, the patient does not have diabetes. Patients should continue to follow a healthy lifestyle and avoid drinking too much sugar or too fast.
The National Diabetes Data Group set a standard for determining diabetes in 1978. Adults were considered to have diabetes if their OGTT results were 11.1 mmol/l or more and their fasting glucose levels were normal. For children, the OGTT result was not sufficient to classify them as having diabetes. However, if they had abnormal OGTT results, they were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
The OGTT is one of the most common screening tests for diabetes. It measures how well the body uses glucose from food. It can determine whether a patient has type 1 diabetes or not, and is also used to screen pregnant women for diabetes. Patients should eat a low-carbohydrate meal before the test. Examples of low-carbohydrate foods include eggs, bacon, cheese, leafy vegetables, and any meat.
OGTT for type 2 diabetes

The current definition of type 2 diabetes is not complete without the OGTT, the oral glucose tolerance test. Although this test has been used since the 1970s, it is considered outdated. However, many doctors are now implementing it to detect T2DM in patients. With the OGTT, the doctor can assess insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in patients. The results of the test can be compared to those of fasting glucose.
A repeat OGTT is not mandatory in the USA. In fact, it is only recommended in patients with diabetes. If an OGTT is not performed annually, 17.8% of diabetic patients would not be identified. Without treatment, the condition can progress further, impairing pulmonary function. Further, patients with CFRD are not aware of their condition. As a result, the disease may be difficult to detect. A recent study showed that patients who had diabetes were diagnosed with the disease.
Self-administered capillary plasma glucose OGTT can screen for T2DM in high-risk Asian adults. The DIY procedure is described as feasible and precise. The result obtained from the test is very close to the results of the laboratory-administered OGTT. Although this procedure may not be perfect, it is a valid alternative to conventional laboratory-administered OGTT for type 2 diabetes.
OGTT for gestational diabetes
The 2 hour glucose tolerance test for gestational diabetic pregnancy can help determine if your baby is likely to develop diabetes. This test involves consuming a sweet drink containing 75 grams of glucose over two hours. A high reading can be indicative of gestational diabetes, but it does not prove that your baby is prone to diabetes. Your doctor can prescribe changes to your diabetes treatment. A glucose tolerance test can be performed early in your pregnancy to avoid the potential risks associated with gestational diabetes.
The tests are often performed in conjunction with other tests to determine if gestational diabetes is present. If your glucose level is borderline or higher than normal, your doctor may recommend a glucose tolerance test. A glucose tolerance test can be performed in people with borderline blood glucose levels, diabetes, hypertriglyceridemia, and retinopathy. The tests are also commonly used to identify perinatal morbidity in pregnancy and to diagnose gestational diabetes. Abnormal glucose metabolism during pregnancy can increase your chances of fetal abnormality and preterm labor.
Before undergoing the test, you must be in good health and active. You should avoid consuming sugary foods and beverages. To ensure that you pass the test without any complications, you should not drink coffee or smoke the night before. You should also try not to eat anything after 10pm on the morning of the test. The test can be stressful, but the results can prove helpful for your health and the health of your baby.
OGTT for prediabetes

If you think you may have prediabetes, you should get an OGTT to determine your glucose level. This test is conducted in a balanced group of people with suspected diabetes and those with neither. It uses the glucose oxidase method to measure glucose levels. A child is given a glucose load of 1.75 g/kg of body weight, up to 75 grams. Then, the person remains seated for 2 hours. After the test, they can return to their usual lifestyle.
The results of the study indicate that the OGTT is useful in identifying patients with prediabetes. A study from a partner obesity facility showed that 167 (28.0%) obese adults had prediabetes and 11.9% were newly diagnosed with diabetes. The study's authors concluded that between 5.6 and 20.7% of the general population met the OGTT's criteria for prediabetes and diabetes, respectively. A further 29% did not meet the criteria for diabetes.
HbA1c and OGTT were associated with the HbA1c result. However, the two tests were not highly correlated. In fact, male sex is more often involved in the HbA1c test. A combination of both tests is more accurate. This may be the best way to identify patients with prediabetes. However, it is not inexpensive. It's important to note that male sex and prediabetes were independently associated with elevated HbA1c levels.