
If you have diabetes, you may be noticing some of the common symptoms in your feet, including pain, numbness, and even ulcers. These conditions can lead to serious health problems, including kidney failure, foot ulcers, and nerve damage. It's important to know how to recognize and treat these symptoms.
Table of Contents
Numbness

Patients suffering from diabetes should visit their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual sensations in their feet. They will conduct a test to determine whether the nerves in the feet are functioning properly. This will include brushing a soft nylon along the foot to determine whether a nerve is damaged. The doctor will check the feet once or twice a year for nerve damage and may refer patients to a foot doctor.
When the blood glucose level is too high, it damages the nerves and blood vessels in the body. The nerves in the feet are particularly delicate, making them vulnerable to damage. Diabetic neuropathy can lead to numbness, pain, and loss of sensation in the feet. It may even lead to ulcers and infection of the feet. If left untreated, the condition may even result in amputation.
The symptoms of diabetes may be difficult to recognize in early stages. Fortunately, there are treatments. A visit to a healthcare provider can help to diagnose and treat diabetes at an early stage. Treatment can include a healthy diet and regular exercise. Exercise helps regulate blood glucose levels and improve circulation.
Neuropathy is one of the most common complications of diabetes. About half of people with diabetes will experience this condition at some point in their lives. The condition can lead to reduced quality of life, poor balance, and fall-related injuries. There are two types of neuropathy: cryptogenic and diabetic sensory neuropathy.
Diabetics symptoms feet numbness can be hard to detect, but it's important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Diabetics can cause the nerves in the feet to die, preventing them from transmitting information to the brain. Consequently, a person with diabetes can experience a lack of sensation in their feet, legs, and hands. They can also develop foot ulcers.
Numbness in the toes
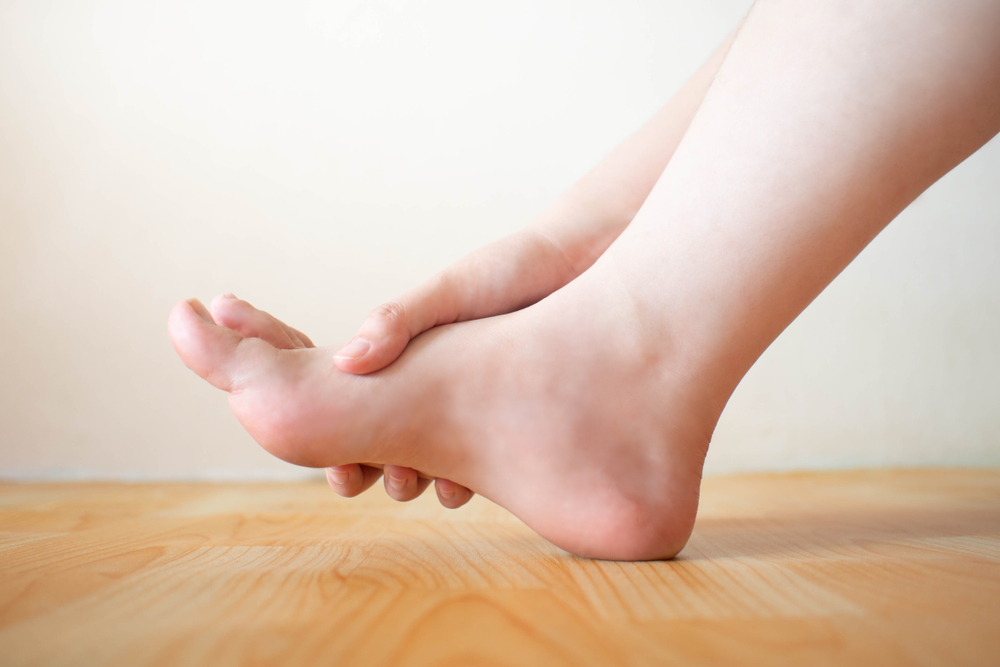

Numbness in the toes as a part of prediabetes symptoms is a warning sign that your blood sugar is too high. Uncontrolled blood sugar can damage the nerves, causing diabetic neuropathy. This can lead to foot ulcers and charcot foot. These ulcers can lead to lower-limb amputation, so it is important to detect the symptoms as soon as possible.
People with diabetes should visit their healthcare provider if they notice any unusual sensations. Their healthcare providers will conduct a test on the nerves in the feet to determine if they are functioning properly. This may involve running a soft nylon along the foot to see if there are any nerve problems. If the test is positive, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a foot doctor to examine the toes.
The nerves in the feet and legs are among the longest in the body. Therefore, when high sugars damage them, they first affect the feet. The arms and hands may be affected later. Moreover, diabetic neuropathy is bi-lateral, meaning that both sides are affected.
Neuropathy can lead to problems with balance and coordination. It can also lead to loss of sensation in the toes. People with diabetes may also develop hammertoe, a condition in which the toes curl under. This condition can cause severe pain.
If you are suffering from diabetes, you should seek medical attention. Numbness in the toes can be a warning sign of more serious symptoms. Diabetes, along with excessive drinking, increases the risk of neuropathy. Approximately one in four people develop neuropathy in their lifetime. If your diabetes is not well-controlled, the high sugar levels can damage the nerves in your hands, feet and legs. It can also lead to foot ulcers.
Foot ulcers
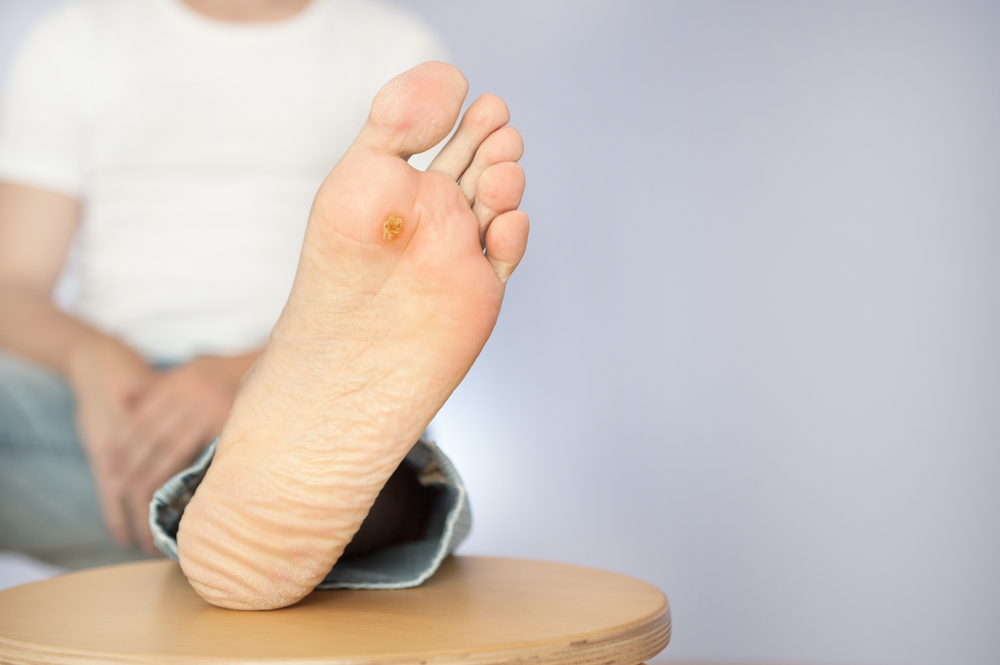

If you are experiencing foot ulcers due to diabetes, you should visit your doctor for a proper diagnosis. Foot ulcers are typically round and have a thick, callused skin surrounding them. Severe ulcers can even expose bones or tendons. The best treatment for foot ulcers is early diagnosis and appropriate medication.
A recent study published in the journal N Engl J Med examined the risk factors for foot ulcers in people with diabetes. The results of the study indicated that people with diabetes were at a higher risk for foot ulcers. The researchers also looked at whether intensive diabetes treatments helped patients avoid foot ulcers.
The development of foot ulcers can be triggered by a simple injury, such as a scrape or cut. However, it can be prevented by proper foot care. People with diabetes should avoid wearing tight shoes to prevent dry skin from developing. It's also important to apply moisturizing lotion to the area to help prevent infection.
In the early stages, foot ulcers can be treated with the right medications and dressings. It is important to clean and bandage the wound daily. A diabetic should not walk barefoot or use crutches if they have a foot ulcer. It is also essential for the patient to keep their blood glucose levels under control.
The most critical aspect of foot ulcer treatment is managing infection. Infected foot ulcers are often life-threatening. The first step is empirical treatment with beta-lactamase inhibitors or cefazolin. Once culture results are available, definitive therapy can be instituted. Infections may require drainage or incision. If the ulcer is deep, surgery may be needed.
Dry skin
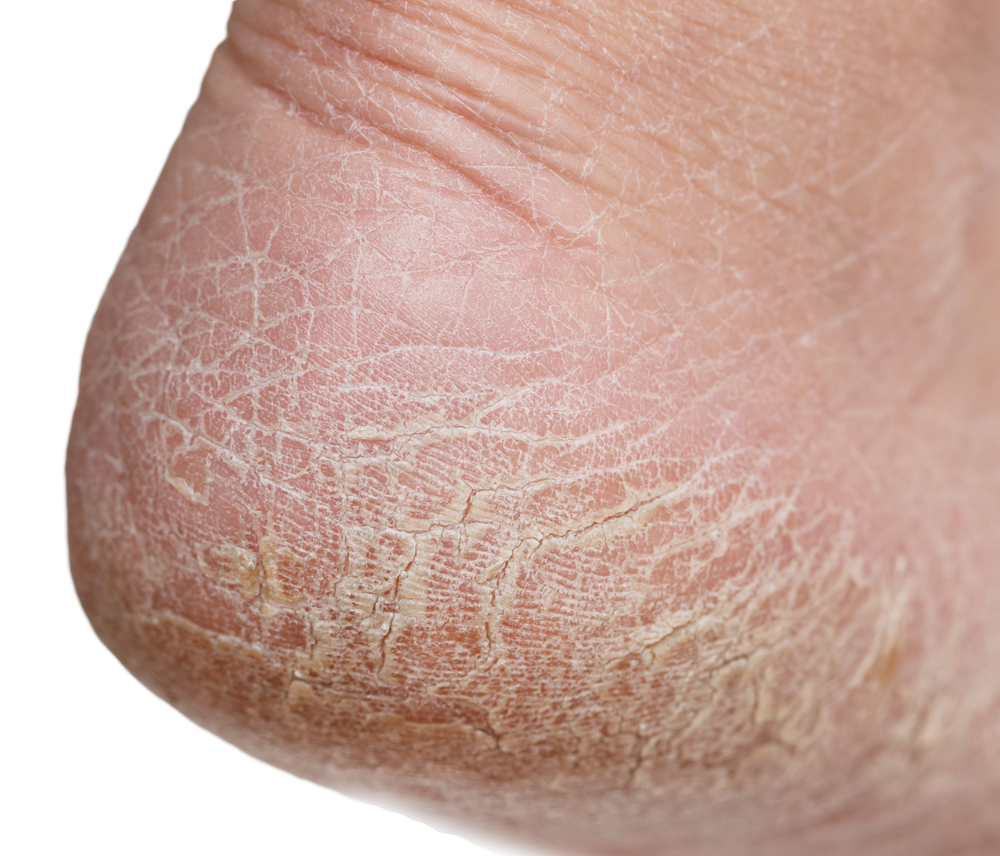
Although dry skin is often an indication of diabetes, it can also be a sign of other health problems. If your skin is dry or itchy, you should visit a dermatologist for a diagnosis. If you have diabetes, you need to take care of your skin year-round to prevent infection and inflammation.
Diabetes is a disease that affects the entire body, but its first signs are typically dermatological. Skin changes that occur during diabetes can be difficult to detect. In some cases, skin problems are not a cause for concern. Others may be just cosmetic. Whatever your skin changes may mean, you should make an appointment with your dermatologist immediately. Some of these changes can be severe, but most are treatable and preventable if detected early.
A high blood sugar level can cause a number of symptoms, including blurred vision, increased urination, and dry skin. You may also experience cracking, redness, and itchiness. Another symptom of poorly-controlled diabetes is frequent bacterial infections. Bacteria flourish in high blood glucose, making you more vulnerable to infection. Infections resulting from diabetes can also affect your skin, including the arms, legs, and groin.
Diabetes also affects the blood vessels, resulting in poor circulation and dry skin. Some common symptoms include brown patches of scaly skin on the legs, itchiness, and poor healing of sores. Dry skin also affects nerves and blood vessels, making your skin more vulnerable to infection.










